Supply chains are intricate webs of processes and components, connecting suppliers, manufacturers, and customers. Understanding the key functions within supply chain management is essential for businesses seeking efficiency and cost-effectiveness. In this article, we will delve into the five major components of supply chain management, highlighting the vital roles they play in modern business operations.
Procurement: The Art of Buying

A. Significance of Procurement
At the heart of every supply chain lies procurement, the process of acquiring the necessary raw materials, goods, and services. Procurement is a cornerstone of supply chain management, as it directly impacts a company's ability to control costs, ensure quality, and meet production demands. Whether it's sourcing materials for manufacturing or obtaining office supplies, effective procurement is crucial to the success of any organization.
B. Types of Procurement: Direct and Indirect
Procurement is often categorized into two main types: direct and indirect. Direct procurement involves the acquisition of raw materials and components needed to create the end product, directly impacting the core operations of a business. Indirect procurement, on the other hand, focuses on obtaining goods and services that support the business's daily functions but are not directly related to the product itself. This distinction is essential as it guides procurement teams in their approach to sourcing and cost management.
C. How Procurement Impacts Cost and Quality of Raw Materials

- Cost Negotiation: Procurement teams negotiate prices with suppliers, striving to secure raw materials at the most competitive rates, which directly affects a company's overall production cost.
- Supplier Selection: The choice of suppliers by procurement professionals can determine the quality of raw materials. Reliable and reputable suppliers typically provide higher-quality materials, reducing the risk of defects and production issues.
- Cost Efficiency: Effective procurement practices aim to optimize the cost of raw materials, ensuring that the company doesn't overpay for essential inputs. This efficiency directly impacts the company's profitability.
- Quality Assurance: Procurement plays a critical role in ensuring that raw materials meet the required quality standards. They often collaborate with quality control teams to establish and maintain quality benchmarks for suppliers.
- Supply Chain Reliability: Procurement teams work to build strong relationships with reliable suppliers, reducing the risk of supply chain disruptions. This reliability is essential for maintaining consistent product quality.
- Cost Reduction Strategies: Procurement professionals employ various strategies, such as bulk purchasing, long-term contracts, and vendor consolidation, to drive down costs while maintaining or improving material quality.
- Risk Mitigation: Procurement teams assess and mitigate risks associated with supplier reliability, quality issues, and market fluctuations. Their risk management efforts aim to maintain consistent material quality and control costs.
- Sustainability and Compliance: Procurement can impact the ethical and environmental aspects of raw materials by selecting suppliers who adhere to sustainability and compliance standards. This ensures that the materials are sourced responsibly and meet regulatory requirements.
- Competitive Advantage: Effective procurement practices can provide a competitive advantage by allowing a company to offer higher-quality products at competitive prices. This can lead to increased market share and customer loyalty.
- Cost of Poor Procurement: Conversely, poor procurement practices can lead to higher production costs, low-quality materials, and disruptions in the supply chain, potentially harming a company's reputation and profitability.
D. The Role of Procurement Teams in Large Organizations
In large organizations, procurement teams have a critical role in optimizing the supply chain. Their responsibilities include supplier selection, negotiations, and managing relationships. By aligning procurement strategies with the overall business objectives, they can significantly impact the company's financial health and operational efficiency.
Inventory Management: Keeping Tabs on Assets
A. The Role of Inventory Management in Managing Materials
Inventory management is a core function within supply chain management, focusing on the control and monitoring of materials and products. It ensures that the right items are available when needed, preventing costly shortages or overstocking issues. Effective inventory management is essential for streamlining operations and meeting customer demands.
B. Methods of Managing Inventory: Physical Inventories and Cycle Counts
Inventory management employs various methods to maintain control. Periodic physical inventories involve physically counting and reconciling all items in stock to verify their accuracy. Cycle counts, on the other hand, are regular, ongoing counts of high-value or high-volume items. These methods are essential for preventing discrepancies and ensuring inventory accuracy.
C. How Technology Aids in Inventory Management
Technology plays a crucial role in modern inventory management. Inventory management software and systems streamline tracking, forecasting, and order replenishment. These tools provide real-time insights into inventory levels, enabling businesses to make informed decisions and avoid costly stockouts or overstocking.
D. The Importance of Efficient Inventory Management for Cost Control
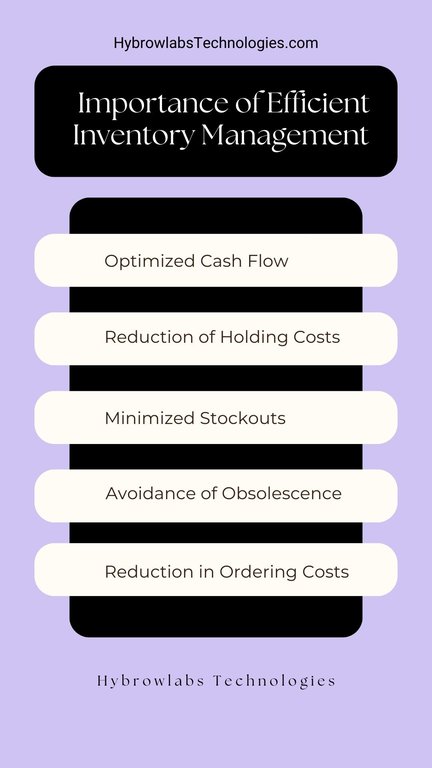
Efficient inventory management not only prevents disruptions in production but also controls costs. Overstocking ties up capital and warehouse space, while understocking results in missed sales and potential customer dissatisfaction. By achieving the right balance, companies can improve cash flow and customer satisfaction.Efficient inventory management is crucial for cost control in several ways:
- Optimized Cash Flow: Maintaining the right inventory levels prevents tying up excessive capital in excess stock, freeing up funds for other crucial business investments.
- Reduction of Holding Costs: Efficient inventory management minimizes the costs associated with storing excess inventory, including warehousing, insurance, and depreciation.
- Minimized Stockouts: By ensuring products are available when needed, inventory management prevents lost sales and potential revenue loss due to stockouts.
- Avoidance of Obsolescence: Excessive inventory can lead to product obsolescence, which results in financial losses. Efficient management helps reduce the risk of holding obsolete items.
- Reduction in Ordering Costs: By accurately predicting inventory needs and reducing the frequency of orders, businesses save on ordering and administrative costs.
- Improved Supplier Negotiations: Efficient inventory management empowers businesses to negotiate better terms with suppliers, potentially securing discounts or favorable credit terms.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Maintaining the right stock levels ensures that customers receive their orders promptly, leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Reduction in Theft and Damage: Excessive inventory increases the risk of theft and damage, while efficient management minimizes these risks, further reducing costs.
- Effective Use of Warehouse Space: Efficient management allows for optimal utilization of warehouse space, reducing the need for additional storage facilities and the associated expenses.
- Streamlined Labor Costs: Proper inventory management ensures that employees' time is used effectively, reducing labor costs associated with unnecessary handling and storage.
Warehouse Management: The Art of Storage and Movement
A. The Distinction Between Warehouse Management and Inventory Management
| Aspect | Warehouse Management | Inventory Management |
| Primary Focus | The physical aspects of storing and moving goods within a warehouse. | Controlling and monitoring inventory levels. |
| Core Responsibilities | - Optimizing the layout of the warehouse. | - Reordering and restocking inventory when levels are low. |
| - Managing storage space efficiently. | - Tracking the quantity of items on hand. | |
| - Ensuring the smooth flow of goods within the warehouse. | - Avoiding overstocking or understocking. | |
| Key Processes | - "Pick, pack, and ship" processes are core components. | - Forecasting demand and managing reorder points. |
| - Managing inbound and outbound shipments. | - Conducting physical inventories and cycle counts. | |
| Role of Technology | Utilizes Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) to optimize processes. | Relies on inventory management software for tracking. |
| May employ technologies like RFID and automation for efficiency. | ||
| Key Benefit | Improves order accuracy, minimizes errors, and reduces lead times. | Ensures products are available when needed, reducing stockouts. |
B. The Importance of Managing the Physical Warehouse and the Flow of Goods
Efficient warehouse management is critical for optimizing the supply chain. It involves organizing the layout of the warehouse, managing storage space, and ensuring the smooth flow of goods. This is essential for reducing lead times, minimizing errors, and meeting customer demands promptly.
C. Key Processes Within Warehouse Management, Such as Pick, Pack, and Ship
The core processes of warehouse management include "pick, pack, and ship." Picking involves selecting the right products from inventory, packing entails preparing them for shipment, and shipping is the final step in sending them to their destination. These processes require careful orchestration to avoid bottlenecks and delays.
D. The Role of Technology in Optimizing Warehouse Management
Modern technology plays a pivotal role in warehouse management. Warehouse management systems (WMS) help streamline processes, track inventory in real-time, and enhance order accuracy. Advanced technologies like RFID, automation, and robotics have revolutionized warehouse operations, making them more efficient and cost-effective.
Manufacturing Operations: Building the Goods
A. The Integral Role of Manufacturing Operations in the Supply Chain
Manufacturing operations form the heart of the supply chain, as this is where raw materials are transformed into finished products. Efficient manufacturing is essential for meeting demand, controlling costs, and ensuring the highest quality standards.
B. How Procurement and Warehouse Management Support Manufacturing
Procurement and warehouse management are critical enablers of manufacturing operations. Procurement ensures the timely availability of raw materials, while warehouse management guarantees their organized storage, easy accessibility, and just-in-time delivery to the manufacturing floor.
C. Tracking Work-in-Progress (WIP) and Quality Control in Manufacturing
Work-in-progress (WIP) tracking is vital in manufacturing. It involves monitoring the status and location of products as they move through various production stages. Quality control is another crucial aspect, ensuring that the products meet defined quality standards before they reach consumers.
D. The Role of Technology in Automating and Managing Manufacturing Operations
Automation and technology have revolutionized manufacturing operations. Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) help control processes, track WIP, and optimize production efficiency. Robotics and AI are increasingly employed to enhance precision, speed, and consistency in manufacturing.
Logistics: Getting Products to Their Destination
A. The Significance of Logistics in Delivering Finished Products

Logistics is the bridge between manufacturing and customers. It encompasses the planning, execution, and control of the movement and storage of goods from the point of origin to the point of consumption. Efficient logistics is crucial for timely deliveries, cost control, and customer satisfaction.
B. Various Modes of Transportation in Logistics, Including Shipping, Air, and Trucking
Logistics offers multiple modes of transportation to suit various needs. For long-distance international shipping, cargo ships are employed. Airfreight is ideal for high-value, time-sensitive goods, while trucking remains a versatile option for regional and local deliveries.
C. Managing Complex Logistics Across Different Countries and Inventories
Cross-border logistics involves managing complex customs regulations, trade compliance, and varying inventory locations. Modern technology, such as global trade management software, simplifies international logistics by automating documentation, tracking, and customs processes.
D. The Impact of Supply Chain Management Technologies on Efficient Logistics
Supply chain management technologies, such as Transportation Management Systems (TMS) and real-time tracking tools, have transformed logistics. These tools optimize route planning, reduce transit times, and enhance visibility, resulting in streamlined operations and reduced costs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the efficient management of warehouses, manufacturing operations, and logistics is integral to the success of any supply chain. By understanding the distinctions and interconnections between these components, businesses can optimize their operations and deliver products to customers promptly and cost-effectively. For more information on supply chain symphony, follow us at hybrowlabs official website.
FAQ
1. What is the primary difference between warehouse management and inventory management?
Warehouse management deals with the physical aspects of storing, organizing, and moving goods within a warehouse, while inventory management focuses on controlling and monitoring inventory levels.
2. How does technology enhance warehouse management?
Warehouse management systems (WMS) and technologies like RFID and automation streamline processes, track inventory in real-time, and improve order accuracy.
3. What is work-in-progress (WIP) tracking in manufacturing operations?
WIP tracking involves monitoring the status and location of products as they move through various production stages to ensure efficient production.
4. How does logistics impact supply chains?
Logistics is crucial for delivering finished products to customers efficiently, involving the planning, execution, and control of the movement and storage of goods.
5. How can supply chain management technologies enhance logistics efficiency?
Technologies like Transportation Management Systems (TMS) and real-time tracking tools optimize route planning, reduce transit times, and enhance visibility in logistics, leading to streamlined operations and reduced costs.



.jpg)


a3dc85.jpg)
.jpg)
fd8f11.png)


.jpg)
.jpg)