The world of cloud computing has revolutionized how businesses work, providing many opportunities for organizations of all sizes to access & handle their IT resources. Among the three main types of cloud computing – SaaS, private cloud & public cloud – each offers a special set of advantages & disadvantages, making it essential for businesses to carefully evaluate their specific requirements before selecting the right cloud model. Today in this blog we will discuss deeply the three main types of cloud computing software & how to choose the right one for the specific requirements in different businesses. So let’s get started!
Main Cloud Computing Software: SaaS, Private Cloud, and Public Cloud:
1. SaaS (Software as a Service):
SaaS is a cloud-based delivery model where software applications are hosted & handled by a third-party provider & users access them through a web browser or API.
2. Private Cloud:
A private cloud is a reliable cloud computing environment owned, handled & utilized by a single organization. It gives the organization complete authority over its data, security & IT infrastructure.
3. Public Cloud:
A public cloud is a shared cloud computing environment where resources are provisioned, operated by a third-party provider & accessed by multiple organizations.
A) SaaS:
SaaS stands for Software as a Service. It is a cloud computing model where software applications are accessed over the internet on a subscription basis. Instead of users installing & maintaining software on their own computers or servers, they can access the software & its characteristics through a web browser. SaaS is one of the three main types of cloud computing, alongside Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS).
Examples of some popular SaaS Software:
- Salesforce: A customer relationship management (CRM) platform that helps businesses handle customer relations, sales & marketing.
- Microsoft 365 (formerly Office 365): Provides a suite of productivity tools like Word, Excel, PowerPoint & collaboration services like SharePoint & Teams.
- Google Workspace (formerly G Suite): Offers a set of productivity & collaboration tools including Gmail, Google Drive, Google Docs & Google Calendar.
- Slack: A messaging & collaboration platform designed for teams, facilitating communication & file sharing.
- Dropbox: A cloud-based file hosting service that allows users to store & share files & folders.
Pros of SaaS Software:
1. Easy Deployment and Maintenance:
Explanation: SaaS solutions are accessible through web browsers, facilitating quick & hassle-free deployment. This ease of accessibility reduces the burden on IT departments for installation & maintenance.
2. Cost-Effectiveness:
Explanation: SaaS operates on a subscription model, offering cost savings by eliminating the need for upfront hardware & software investments. Organizations pay for the services they use, promoting financial efficiency.
3. Regular Updates and Innovation:
Explanation: SaaS providers handle maintenance, updates & feature enhancements centrally. This ensures that users consistently have access to the latest functionalities, security patches & innovations without requiring manual intervention.
Cons of SaaS Software:
1. Limited Customization:
Explanation: SaaS applications may have limitations in customization. Organizations might find it challenging to tailor the software to specific operational needs, as the service provider often predetermines customization options.
2. Vendor Lock-in:
Explanation: Transitioning away from a SaaS provider can be complicated due to proprietary data formats & integration complexities. This can potentially limit an organization's flexibility to switch to alternative solutions.
3. Security Concerns:
Explanation: Storing data with a third party raises security concerns. Organizations need assurance that the SaaS provider employs robust security measures to protect sensitive information & ensure compliance with data privacy regulations.
B) Private Clouds:

A private cloud refers to a cloud computing environment exclusively used by a single organization. Unlike public clouds, which are shared by multiple organizations & hosted by third-party providers, a private cloud is typically owned, operated & maintained by the organization it serves. This type of cloud infrastructure provides greater control & customization over resources & security.
Popular examples of Private Cloud Software:
- VMware vCloud Suite: Offers a comprehensive set of software-defined data center (SDDC) technologies, allowing organizations to build & manage private clouds.
- OpenStack: An open-source cloud computing platform that allows the deployment & management of private & public clouds.
- Microsoft Azure Stack: An extension of Microsoft Azure, Azure Stack allows organizations to run Azure services on-premises or in a hosted environment.
- IBM Cloud Private: Provides a platform for creating, deploying & handling applications on-premises or in private clouds.
Pros of Private Cloud Software:
1. Enhanced Security and Control:
Private clouds offer a high level of control over security measures & data, making them suitable for organizations with strict security & compliance requirements. This enhanced control enhances data protection.
2. Tailored Customization:
Organizations can customize a private cloud to meet specific business needs. This flexibility allows for the creation of an infrastructure that aligns seamlessly with unique operational requirements.
3. Flexibility to Adapt to Unique Needs:
Private clouds provide flexibility, enabling organizations to adapt the infrastructure to unique business needs. This is particularly beneficial for industries with specific compliance, regulatory, or performance requirements.
Cons of Private Cloud Software:
1. Higher Upfront Costs:
Establishing a private cloud infrastructure involves significant upfront investments in hardware, software & implementation. This capital-intensive nature can be a barrier for some organizations.
2. Requires In-House Expertise:
Managing a private cloud demands skilled IT personnel. Organizations may need to invest in training or hiring experts to handle the complexities of private cloud infrastructure.
3. Scalability Limitations:
Scaling a private cloud can be more complex than scaling in a public cloud. Organizations may face limitations in rapidly adjusting resources to accommodate fluctuating workloads.
Private clouds are often chosen by organizations with specific regulatory compliance requirements, a need for greater control over their IT infrastructure, or those handling sensitive data that requires heightened security measures. While private clouds offer advantages in terms of control & security, they may involve higher upfront costs & require more management and maintenance compared to public cloud solutions.
C) Public Cloud:
A public cloud refers to a cloud computing model where computing services & resources are offered over the internet by third-party providers. These services are made available to the general public & users can access and utilize them on a pay-as-you-go or subscription basis. Public cloud providers own, operate & maintain the infrastructure, making it a shared & scalable resource for multiple organizations & users.
Some popular examples of Public Cloud Software:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): It offers a wide range of cloud computing services, including computing power, storage, databases, machine learning, analytics & more.
- Microsoft Azure: Microsoft Azure provides a comprehensive set of cloud services, including virtual machines, app services, databases & AI services, along with integration with Microsoft's software products.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): It offers services for computing, storage, databases, machine learning & big data analytics, leveraging Google's infrastructure & technology.
- IBM Cloud: IBM Cloud provides a suite of cloud services, including infrastructure like service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS) & software as a service (SaaS), along with AI and data analytics.
Pros of Public Clouds Software:
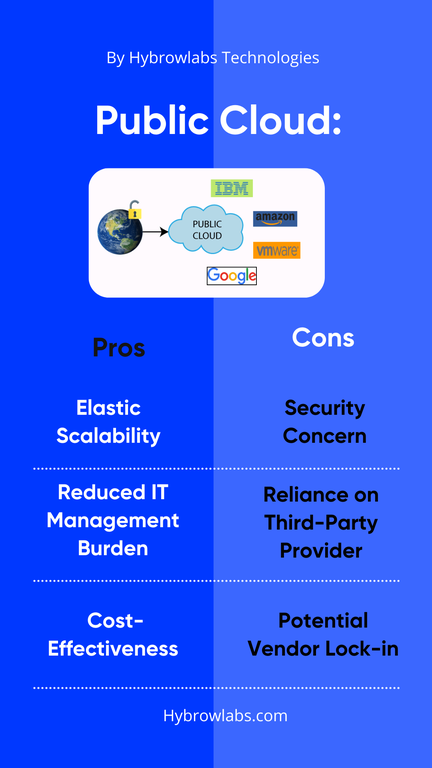
1. Elastic Scalability and Flexibility:
Public clouds offer on-demand scalability, allowing organizations to scale resources up or down based on demand. This elasticity ensures efficient handling of variable workloads.
2. Reduced IT Management Burden:
Public cloud providers handle infrastructure maintenance & management, reducing the burden on internal IT teams. This allows organizations to focus on strategic initiatives rather than day-to-day operational tasks.
3. Cost-Effectiveness for Fluctuating Workloads:
Pay-as-you-go pricing in public clouds allows organizations to pay only for the resources they consume. This cost-effective model is particularly advantageous for businesses with variable workloads.
Cons of Public Clouds Software:
1. Security and Data Privacy Concerns:
Organizations may have concerns about the security of data stored in a third-party's infrastructure. A comprehensive assessment of the chosen provider's security measures is crucial to ensure data integrity & privacy.
2. Reliance on Third-Party Provider:
Organizations using public clouds are dependent on the reliability and performance of the third-party provider. Downtime or service disruptions on the provider's end can impact the organization's operations.
3. Potential Vendor Lock-in:
Switching between public cloud providers can be challenging due to differences in services, APIs & data formats. Organizations may find themselves locked into a specific provider, limiting their flexibility & negotiation power.
The Key Differences Between SaaS, Private Cloud & Public Cloud:
| Aspect | SaaS (Software as a Service) | Private Cloud | Public Cloud |
| Deployment Model | Access via web browser. | On-premises or hosted by a third party. | Accessible over the internet from anywhere. |
| Ownership and Control | Managed by a third-party provider. | Owned & controlled by the organization. | Owned & operated by third-party providers. |
| Customization | Limited customization. | High level of customization. | Variable customization based on the service. |
| Cost Structure | Subscription-based. | Capital-intensive with upfront costs. | Pay-as-you-go or subscription-based. |
| Maintenance Responsibility | Managed by the service provider. | Responsibility is shared between the organization & the provider. | Managed by the third-party provider. |
| Scalability | Typically easily scalable. | Scalable but may have limitations. | Highly scalable with on-demand resources. |
| Security Control | Relies on the security measures implemented by the service provider. | Offers enhanced security control, especially for compliance needs. | Security is managed by a third-party provider. |
| Flexibility | Limited flexibility for unique needs. | Adaptable to unique business requirements. | High flexibility & adaptability. |
| Dependency on In-House Expertise | Minimal need for in-house expertise. | Requires skilled personnel for management & customization. | Relies on the expertise of the cloud provider. |
| Data Privacy Concerns | Concerns may arise due to third-party data management. | Controlled and managed in-house, reducing external privacy concerns. | Concerns exist & organizations need to assess the provider's data privacy measures. |
| Vendor Lock-in | Potential for lock-in due to data format differences and integration complexities. | Limited lock-in; organizations have control over their infrastructure. | Potential lock-in due to differences in services, APIs & data formats. |
Selecting the Right Cloud Model for Your Needs:

Choosing the right cloud computing model for your organization's needs is a critical decision that can significantly impact your IT infrastructure, business agility & overall success. To make an informed decision, it's essential to carefully evaluate your specific requirements, consider the pros & cons of each cloud model & align your choice with your long-term strategic goals.
Factors to Consider when Choosing a Cloud Model:
1. Business Needs and Goals:
Clearly define your organization's business objectives & IT requirements. Consider aspects like data security, scalability, customization & cost-effectiveness.
2. Application Requirements:
Identify the types of applications & workloads you plan to deploy in the cloud. Consider factors like performance, sensitivity of data & integration with existing systems.
3. IT Expertise and Resources:
Assess your organization's internal IT capabilities & expertise in managing cloud infrastructure. Consider the availability of skilled IT professionals to handle cloud deployment, maintenance & security.
4. Budget and Cost Considerations:
Evaluate the upfront & ongoing costs associated with each cloud model, including infrastructure investments, software licenses, maintenance fees & potential vendor lock-in scenarios.
5. Data Security and Privacy Compliance:
Assess the level of data security & privacy requirements for your organization. Consider industry regulations, data sensitivity & the provider's data handling practices.
6. Scalability and Flexibility:
Evaluate your organization's future growth projections & the need for scalable IT infrastructure. Consider the ability of the cloud model to accommodate fluctuating workloads & adapt to changing business needs.
Selecting the Right Cloud Model:
- SaaS (Software as a Service): Suitable for organizations seeking a cost-effective, easy-to-deploy solution with limited customization needs. Ideal for non-critical applications, standardized workflows & businesses with limited IT resources.
- Private Cloud: Ideal for organizations requiring high levels of control, security & customization over their IT infrastructure. Suitable for sensitive data, compliance-driven industries & organizations with in-house IT expertise.
- Public Cloud: A good choice for organizations seeking elastic scalability, pay-as-you-go pricing & access to a vast pool of resources. Suitable for fluctuating workloads, rapid deployment & businesses with a focus on innovation & agility.
- Hybrid Cloud: A combination of private & public cloud environments, providing flexibility & control for critical applications while leveraging the cost-effectiveness & scalability of public cloud for non-critical workloads.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the organizations navigating this technological opera – must weigh the benefits & drawbacks, considering factors like customization, control, costs & security. Unraveling the threads of SaaS, Private Cloud, and Public Cloud Software reveals a spectrum of possibilities, enabling organizations to curate their own narrative of success in the ever-evolving world of digital transformation. To continue your successful Cloud Computing journey partner with Hybrowlabs, we assure your success in this severely competitive market. If you are looking for a great partnership to help you in your Digital Transformation journey for your business then you are at the right place. We at Hybrowlabs are ready to take the necessary steps to help you achieve your goals. Why are you waiting for? Connect with our expert developers and discuss the path of solution for all of your problems.
More Read- Crucial digital transformation insights from Amazon's case study.
FAQ:
1. What is SaaS, and how does it differ from traditional software?
SaaS is a cloud computing model that delivers software applications over the internet. Unlike traditional software, SaaS is accessed through a web browser without the need for local installations.
2. What are the key benefits of implementing a private cloud infrastructure?
Private clouds offer enhanced security & control, tailored customization, and flexibility to adapt to unique organizational needs.
3. What is the primary advantage of using a public cloud for computing needs?
The primary advantage is elastic scalability & flexibility. Public clouds allow organizations to scale resources up or down based on demand, providing cost-effectiveness & adaptability.
4. How can organizations ensure data privacy and security when using public cloud services?
To ensure data privacy & security, organizations should carefully select a reputable cloud provider with strong security measures, implement encryption & regularly monitor and audit data activities.
5. Is there a risk of vendor lock-in when utilizing public cloud services?
Yes, there is a potential risk of vendor lock-in due to differences in services, APIs & data formats among cloud providers. Organizations should consider this & plan for potential migration strategies.



4df9a2.png)


a3dc85.jpg)

.jpg)
fd8f11.png)

.jpg)
.jpg)